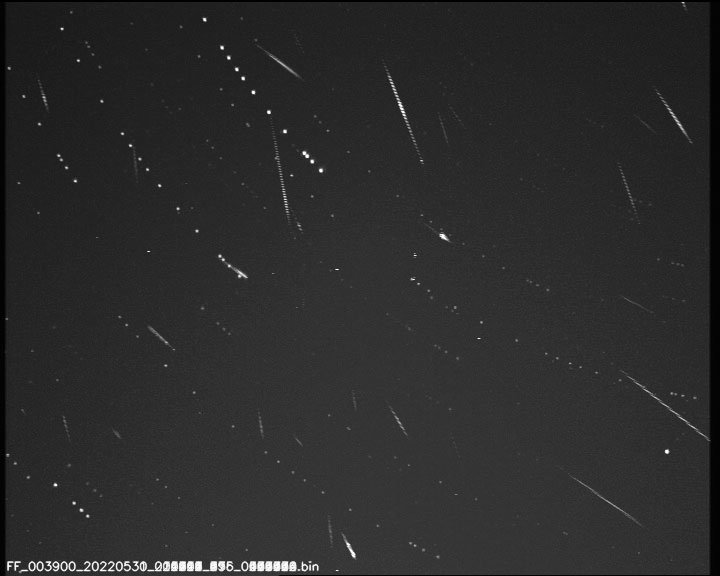
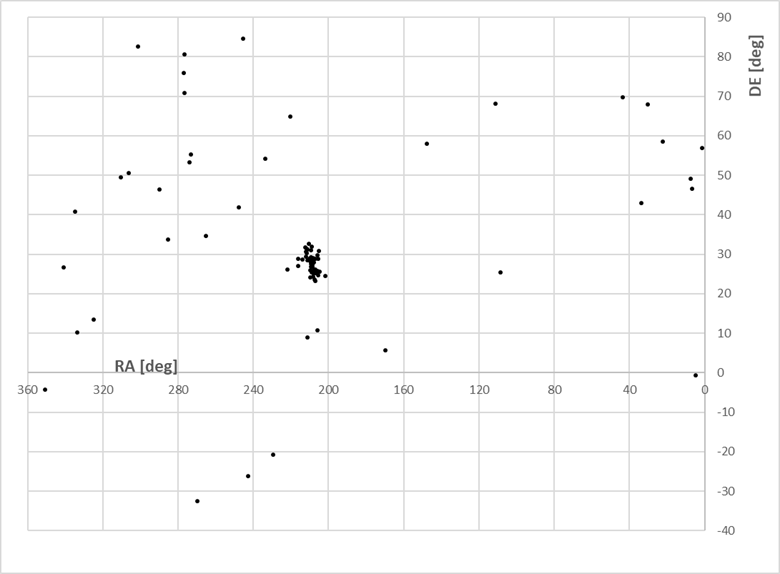
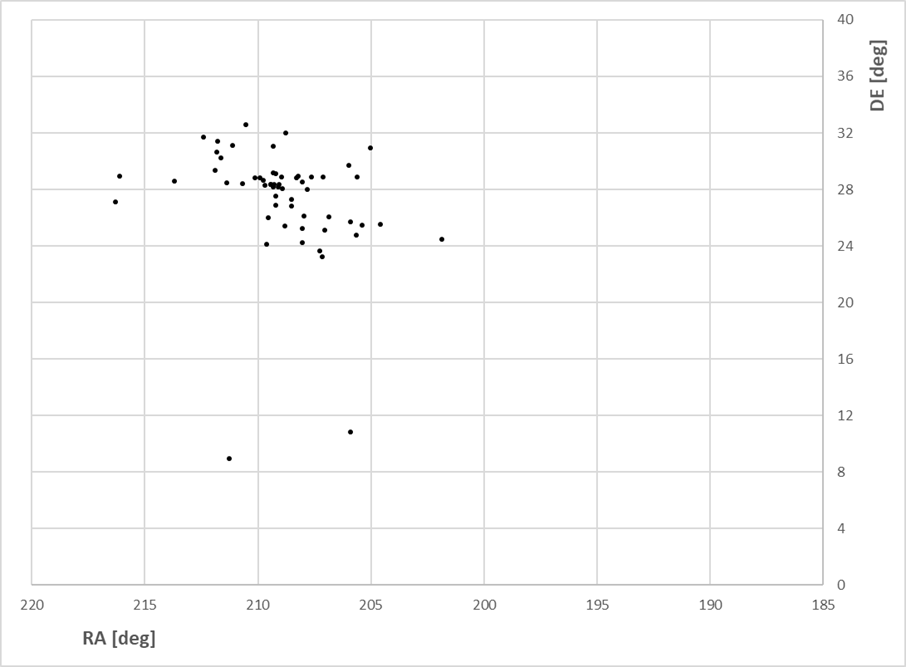
Alerte d'activité des Tau Herc le 31/05 au petit matin, la France est un peu mal placée hélas
Electronic Telegram No. 5125
Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams
Mailing address: Hoffman Lab 209; Harvard University;
20 Oxford St.; Cambridge, MA 02138; U.S.A.
e-mail: cbatiau@eps.harvard.edu (alternate cbat@iau.org)
URL http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/index.html
Prepared using the Tamkin Foundation Computer Network
TAU HERCULID METEOR SHOWER 2022
P. Jenniskens, SETI Institute and NASA Ames Research Center; Q. Ye,
University of Maryland and Boston University; and J. Vaubaillon, I.M.C.C.E,
Observatory of Paris, report that a meteor outburst of tau Herculid meteors
(IAU shower 61) is anticipated for May 31 around 4h-5h UT this year. This
outburst is unusual in that the debris was generated during the 1995 breakup
of comet 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann (cf., Luethen et al. 2001, J. Intl. Meteor
Organization 29, 15-28). Independent calculations at I.M.C.C.E. and the
University of Maryland, using slightly different inputs, now put the 1995
dust trail in the earth's path with an expected peak on May 31d05h01m and
03h52m UT, respectively. In both models, meteors will radiate from R.A. =
209 deg, Decl. = +28 degrees with an apparent velocity of 16.4 km/s
(geocentric velocity 12.1 km/s). The outburst is expected to last about two
hours. Observers in the continental USA and Mexico are most favorably
located to see this event in new-moon conditions, with a radiant high in the
northwest.
The authors note that there are two caveats. First, an unusual meteor
shower will only happen if the meteoroid ejection velocities during the
breakup and decay of fragments were a factor of 2.5 higher than under normal
cometary ejection conditions. Because the comet itself is not near the earth,
normal ejection does not have the meteoroids disperse far enough ahead of the
comet to intersect the earth's path. The higher gas-production rate of comet
73P in 1995 suggests that ejection velocities may have been higher by up to a
factor of 2.7. However, the ejection velocities of cm- and mm-sized
meteoroids were not measured in 1995. Second, if the outburst happens, the
meteors will be mostly faint. Rare tau Herculids are also known from regular
cometary activity during normal returns. The Cameras for Allsky Meteor
Surveillance (CAMS) project, which triangulates video-detected meteors visible
to the naked eye, measured the orbit of 18 tau Herculids during dust-trail
crossings in 2011, 2017/ and 2019; from this, the authors calculate a steep
magnitude-distribution index of 5.4 +/- 1.1, meaning that there were five
times more meteors of magnitude +4 than +3, five times more meteors of mag
+3 than +2, etc. -- but with the camera sensitivity such that more meteors of
magnitude +3 were detected. In practice, a few meteors were of magnitude +1,
but most were near the +4 magnitude detection limit of the video cameras.
Calculations at the University of Maryland show that when the earth
crosses the meteoroid stream, a very faint glow from scattered sunlight may be
visible in the sky centered around R.A. = 170 deg, Decl. = +20 deg in Leo,
and around R.A. = 355 deg, Decl. = -15 deg in the opposite direction in Equ.
Finally, two dust trails from the normal 1892 and 1897 returns of 73P will
also be in the earth's path around 16h UT on May 30 and 10h UT on May 31,
respectively (cf., Wiegert et al. 2005, MNRAS 361, 638). Because the comet
has been known only since 1930, these trail crossings could shed new light
onto the past activity of the comet, if detected.
NOTE: These 'Central Bureau Electronic Telegrams' are sometimes
superseded by text appearing later in the printed IAU Circulars.
(C) Copyright 2022 CBAT
2022 May 26 (CBET 5125) Daniel W. E. Green
Electronic Telegram No. 5125
Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams
Mailing address: Hoffman Lab 209; Harvard University;
20 Oxford St.; Cambridge, MA 02138; U.S.A.
e-mail: cbatiau@eps.harvard.edu (alternate cbat@iau.org)
URL http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/index.html
Prepared using the Tamkin Foundation Computer Network
TAU HERCULID METEOR SHOWER 2022
P. Jenniskens, SETI Institute and NASA Ames Research Center; Q. Ye,
University of Maryland and Boston University; and J. Vaubaillon, I.M.C.C.E,
Observatory of Paris, report that a meteor outburst of tau Herculid meteors
(IAU shower 61) is anticipated for May 31 around 4h-5h UT this year. This
outburst is unusual in that the debris was generated during the 1995 breakup
of comet 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann (cf., Luethen et al. 2001, J. Intl. Meteor
Organization 29, 15-28). Independent calculations at I.M.C.C.E. and the
University of Maryland, using slightly different inputs, now put the 1995
dust trail in the earth's path with an expected peak on May 31d05h01m and
03h52m UT, respectively. In both models, meteors will radiate from R.A. =
209 deg, Decl. = +28 degrees with an apparent velocity of 16.4 km/s
(geocentric velocity 12.1 km/s). The outburst is expected to last about two
hours. Observers in the continental USA and Mexico are most favorably
located to see this event in new-moon conditions, with a radiant high in the
northwest.
The authors note that there are two caveats. First, an unusual meteor
shower will only happen if the meteoroid ejection velocities during the
breakup and decay of fragments were a factor of 2.5 higher than under normal
cometary ejection conditions. Because the comet itself is not near the earth,
normal ejection does not have the meteoroids disperse far enough ahead of the
comet to intersect the earth's path. The higher gas-production rate of comet
73P in 1995 suggests that ejection velocities may have been higher by up to a
factor of 2.7. However, the ejection velocities of cm- and mm-sized
meteoroids were not measured in 1995. Second, if the outburst happens, the
meteors will be mostly faint. Rare tau Herculids are also known from regular
cometary activity during normal returns. The Cameras for Allsky Meteor
Surveillance (CAMS) project, which triangulates video-detected meteors visible
to the naked eye, measured the orbit of 18 tau Herculids during dust-trail
crossings in 2011, 2017/ and 2019; from this, the authors calculate a steep
magnitude-distribution index of 5.4 +/- 1.1, meaning that there were five
times more meteors of magnitude +4 than +3, five times more meteors of mag
+3 than +2, etc. -- but with the camera sensitivity such that more meteors of
magnitude +3 were detected. In practice, a few meteors were of magnitude +1,
but most were near the +4 magnitude detection limit of the video cameras.
Calculations at the University of Maryland show that when the earth
crosses the meteoroid stream, a very faint glow from scattered sunlight may be
visible in the sky centered around R.A. = 170 deg, Decl. = +20 deg in Leo,
and around R.A. = 355 deg, Decl. = -15 deg in the opposite direction in Equ.
Finally, two dust trails from the normal 1892 and 1897 returns of 73P will
also be in the earth's path around 16h UT on May 30 and 10h UT on May 31,
respectively (cf., Wiegert et al. 2005, MNRAS 361, 638). Because the comet
has been known only since 1930, these trail crossings could shed new light
onto the past activity of the comet, if detected.
NOTE: These 'Central Bureau Electronic Telegrams' are sometimes
superseded by text appearing later in the printed IAU Circulars.
(C) Copyright 2022 CBAT
2022 May 26 (CBET 5125) Daniel W. E. Green
 Accueil
Accueil